Uterine fibroids (leiomyomas or myomas) are benign (non-cancerous) smooth muscle tumors that develop in the uterus. They are common in women of reproductive age and can vary in size, number, and location within the uterus.



A 36-year-old female presented with severe pelvic pain, heavy menstrual bleeding with clots. She had a constant heaviness in pelvic region since last 2 months associated with thick, white leucorrhea daily. Her Ultrasound report was as follows:
- Uterus: Shows multiple fibroids (largest 16 × 12 mm)
- Uterus: bulky, adenomyosis
- Cervix: bulky suggestive of cervicitis
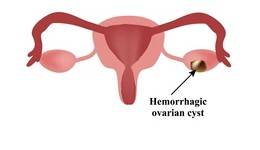
- Bilateral PCOD (polycystic ovarian morphology)
After 6 months of Homoeopathic Treatment
- Normal-sized uterus with no fibroids observed.
- Normal cervix.
- Normal ovaries and adnexae.
Causes and Risk Factors:
- Hormonal Imbalance: Estrogen and progesterone promote fibroid growth.
- Genetics: Family history increases the risk.
- Race: More common in African American women.
- Obesity: Higher estrogen levels can contribute.
- Diet & Lifestyle: High red meat intake and low vitamin D levels may be linked.
Types of Fibroids:
- Intramural: Within the uterine wall (most common).
- Subserosal: Grow on the outer surface of the uterus.
- Submucosal: Protrude into the uterine cavity (can cause heavy bleeding).
- Pedunculated: Attached to the uterus by a stalk.
Symptoms:
- Heavy or prolonged menstrual bleeding
- Pelvic pain or pressure
- Frequent urination or difficulty emptying the bladder
- Constipation
- Backache or leg pain
- Infertility or pregnancy complications in some cases
Diagnosis:
- Ultrasound (USG): First-line imaging.
- MRI: Provides more detailed imaging.
- Hysteroscopy/Sonohysterography: Useful for submucosal fibroids.
Treatment Options:
- Medical Management:
- Hormonal therapy (e.g., birth control pills, GnRH agonists)
- NSAIDs for pain relief
- Tranexamic acid for heavy bleeding
- Surgical Management:
- Myomectomy: Removal of fibroids while preserving the uterus (for fertility preservation).
- Hysterectomy: Complete removal of the uterus (definitive treatment for symptomatic cases).
Prognosis:
- Fibroids may shrink after menopause.
- Proper treatment can effectively manage symptoms.
- Recurrence is possible, especially after myomectomy.
Lifestyle & Dietary Recommendations:
- Diet: Increase iron-rich foods (beetroot, spinach, jaggery) to prevent anemia.
- Hydration: Drink plenty of water to prevent estrogen dominance.
- Exercise: Light yoga and walking help with circulation.
- Stress Management: Meditation and relaxation techniques reduce hormonal imbalances.
Homeopathic Perspective:
Individualized treatment based on totality of symptoms.
Focus on constitutional remedy to prevent recurrence.
Schedule an appointment with us?
Interested in reading more about other cases cured at RG’s Homoeopathy?