A hemorrhagic ovarian cyst (HOC) is a functional cyst that forms when a blood vessel within the ovarian follicle ruptures, causing blood to accumulate inside. These cysts are common but larger cysts can cause significant discomfort and complications.
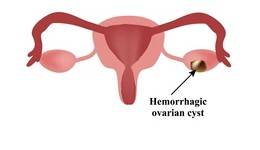


A 20 year old female visits the clinic with pelvic pain, dysmenorrhea and irregular menstrual cycle. Her ultrasound reports showed the following findings
- Left Ovarian Hemorrhagic Cyst (~56 × 36 mm) with dense internal echoes and thick echogenic debris.
- Grade I Fatty Liver (~14.2 cm)
- Gastritis
After 6 months of Homoeopathic Treatment
- Left ovarian hemorrhagic cyst resolved.
- No signs of fatty liver.
- Gastritis improved.
- Overall abdominal health restored with no abnormal findings.
Causes
- Hormonal Imbalance – Irregular ovulation or excessive estrogen production.
- Menstrual Cycle Variations – Often seen in women of reproductive age.
- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) – Increases the risk of cyst formation.
- Endometriosis – Endometrial tissue may form cystic lesions filled with blood.
- Use of Fertility Drugs – Can lead to excessive ovarian stimulation.
Symptoms:
- Pelvic Pain – Often on one side, worsening during menstruation.
- Lower Abdominal Heaviness – A sensation of pressure.
- Irregular Menstrual Cycles – Due to hormonal fluctuations.
- Painful Intercourse (Dyspareunia) – Especially deep penetration.
- Frequent Urination or Bowel Issues – Due to pressure on surrounding organs.
- Rupture Symptoms – Sudden severe pain, dizziness, nausea, or internal bleeding (in rare cases).




Prognosis and Possible Complications
- Rupture or Bleeding: Large cysts may burst, leading to internal bleeding and requiring emergency care.
- Torsion: A large cyst may twist the ovary, cutting off blood supply and causing severe pain.
- Chronic Pain or Adhesions: In some cases, repeated cyst formation can lead to pelvic adhesions.
Impact on Daily Life
- Pain and Discomfort – Can affect routine activities, including work and exercise.
- Emotional Stress – Anxiety related to menstrual irregularities and fertility concerns.
- Sexual Dysfunction – Pain during intercourse may affect relationships.
- Reduced Energy Levels – Chronic pelvic pain can lead to fatigue.
Conventional Treatment Approaches
- Observation: Small cysts are monitored through ultrasound.
- Pain Management: NSAIDs like ibuprofen to relieve pain.
- Hormonal Therapy: Birth control pills to prevent cyst formation.
Surgical Intervention:
- Cystectomy – Removal of the cyst while preserving the ovary.
- Oophorectomy – Removal of the ovary if necessary.
- Emergency Surgery – Required if rupture leads to internal bleeding.
Homeopathic Perspective:
An individualized treatment based on totality of symptoms focuses on:
- Reducing pain and inflammation naturally.
- Dissolving existing cysts and preventing recurrence.
- Balancing hormonal fluctuations to promote regular ovulation.
- Prescribing a constitutional remedy to prevent recurrence.
Schedule an appointment with us?
Interested in reading more about other cases cured at RG’s Homoeopathy?